
The null hypothesis determines the values of the population parameter at which the null hypothesis is rejected. The alternative hypothesis, denoted H 1, is a contradiction of the null hypothesis.
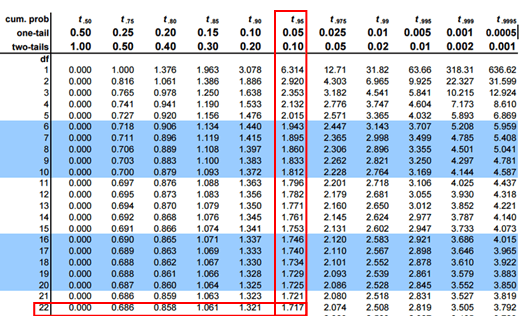
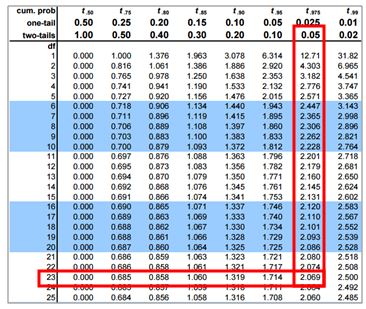
\(μ_0\)= the hypothesized population mean. H 0: Each 1 kg package has 0.15% cholesterol.Ī test would then be carried out to confirm or reject the null hypothesis. The inspectors will formulate a hypothesis like: In other words, it represents the “status quo.” For example, the U.S Food and Drug Administration may walk into a cooking oil manufacturing plant intending to confirm that each 1 kg oil package has, say, 0.15% cholesterol and not more. The null hypothesis, denoted as H 0, represents the current state of knowledge about the population parameter that’s the subject of the test. It brings out the notion that “there is nothing about the data.” The null hypothesis is the statement concerning the population parameter values. The size of the hypothesis test and errorsĪs stated earlier, the first stage of the hypothesis test is the statement of the null hypothesis.The elements of the test hypothesis include: The critical values are determined by the distribution of the test statistic (when the null hypothesis is true) and the size of the test (which gives the size at which we reject the null hypothesis). On the other hand, the alternative hypothesis states the parameter values (critical values) at which the null hypothesis is rejected. The null hypothesis is an assumption of the population parameter.
Hypothesis testing starts by stating the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. Hypothesis testing tries to test whether the observed data of the hypothesis is true. Hypothesis testing is defined as a process of determining whether a hypothesis is in line with the sample data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
